Balance Sheet Components
-
What Are Assets?
-
What Are Liabilities?
-
What Is Equity?
Balance
Sheet Components
The Balance Sheet is one of
the core financial statements and shows what a business owns, owes,
and what’s left for the owner—at a specific point in time. It’s like a
financial snapshot of the business’s health.
“A Balance Sheet summarizes a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity based on the accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.”
This report helps owners, investors, and lenders understand how stable and solvent a business really is.
“A Balance Sheet summarizes a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity based on the accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.”
This report helps owners, investors, and lenders understand how stable and solvent a business really is.
1. What Are Assets?
Assets are everything the business owns that has
value and can help generate income. This includes cash in hand or in the bank, accounts receivable (money
customers owe the business), inventory
(products waiting to be sold), and equipment or vehicles
used in daily operations. It also includes prepaid
expenses, like insurance or rent paid in advance. Assets are
generally divided into two categories: current assets,
which are expected to be used or converted into cash within one year (such as
cash, receivables, and short-term investments), and non-current assets, which are
long-term in nature, like buildings, land, or machinery.
2. What Are Liabilities?
Double-entry bookkeeping is the standard method used by most
businesses worldwide. In this system, every financial transaction affects at
least two accounts—one is debited, and the other is credited. This method is
based on the fundamental accounting equation: Assets
= Liabilities + Equity. For example, if you sell a product for
$100 in cash, you would record a debit to Cash
(which increases your assets) and a credit to Sales
(which increases your income). This dual effect helps keep the books balanced
and minimizes the chance of errors. It also provides a more complete and
accurate view of a business’s financial health, making it essential for
generating reports like the Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss Statement.
3.
What Is Equity?
Equity represents the owner's claim on the business
after all debts and liabilities have been settled. It includes the owner’s capital, which is the
money invested into the business; retained earnings,
which are the profits that have been kept in the business rather than
withdrawn; and owner’s drawings,
which reflect any money the owner has taken out for personal use. Equity shows
what portion of the business truly belongs to the owner. In simple terms, it
fits into the accounting equation: Assets (what you have) =
Liabilities (what you owe) + Equity (what you own). This
balance ensures that every dollar in the business is accounted for—either
through what it owes or what it owns.
4. Real-Life Example
If a business owns $20,000 in assets
(like cash and inventory), and owes $8,000 in liabilities (like bills and
loans), the equity is: $20,000 - $8,000 = $12,000
That $12,000 represents the owner’s stake in the business.
That $12,000 represents the owner’s stake in the business.
Key Takeaways
✅ The Balance Sheet shows assets, liabilities, and equity at
a specific point in time.
✅ Assets = Liabilities + Equity — this equation must always stay balanced.
✅ Assets are what the business owns; liabilities are what it owes.
✅ Equity is what remains for the owner after liabilities are paid.
✅ The Balance Sheet helps assess financial health, liquidity, and stability.
✅ Assets = Liabilities + Equity — this equation must always stay balanced.
✅ Assets are what the business owns; liabilities are what it owes.
✅ Equity is what remains for the owner after liabilities are paid.
✅ The Balance Sheet helps assess financial health, liquidity, and stability.
Write your awesome label here.
Access all Accounting and Bookkeeping Courses from One Portal.
Mastering Bookkeeping and Accounting
MBA simplifies accounting, ledger management, account balancing and financial statement preparation.
QuickBooks Online For Bookkeepers
From Beginner to Expert: Master QuickBooks Online. Effortlessly Navigate, Analyze Transactions, and Unlock its Full Potential.
Xero Accounting For Bookkeepers
Learn how to use Xero, the leading online accounting software to perform most of the essential bookkeeping tasks.
ChatGpt for Bookkeepers and Accountants
Learn how to use the ChatGPT prompt toolkit to simplify daily accounting tasks for accountants and bookkeepers instantly.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay informed with the latest accounting tips, tools, and updates from Accountutor right in your email inbox.
Thank you!
Policy Pages

Download QuickBooks Online PDF Guide
Thank you!

Download QuickBooks Online Cheat Sheet
Thank you!

Download ABCD of Accounting
Thank you!

Download Checklist 2024
Thank you!
Register For Free!
Thank you!
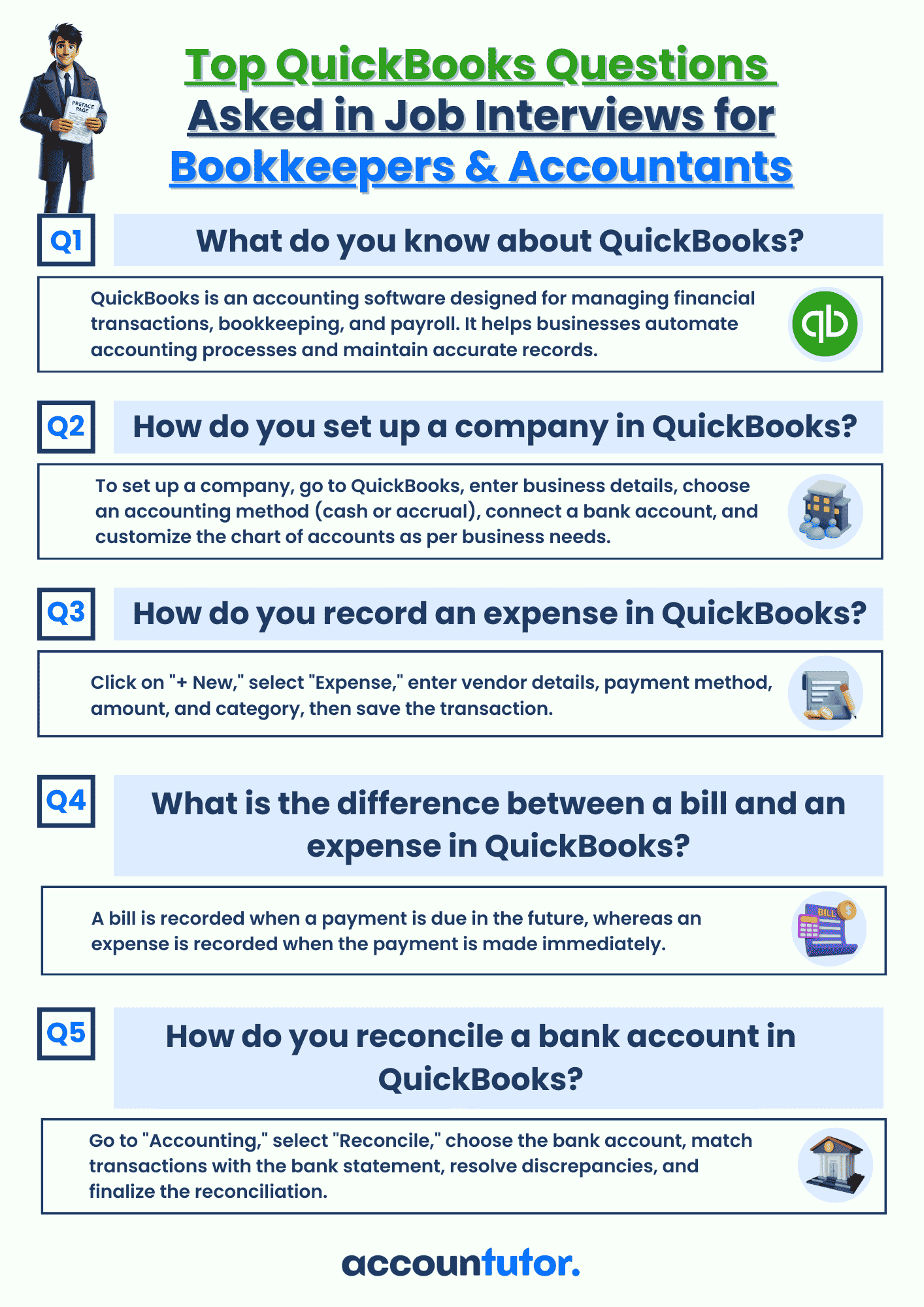
Download Interview Questions
Thank you!

